
-
This photograph of a polar bear, one of the wildlife species that may benefit from President Barack Obama’s decision, was taken by Terry DeBruhn. Image courtesy U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service.
Relying on a statute from the 1950s, President Barack Obama moved Tuesday to permanently shut off the Arctic and a significant portion of the Atlantic oceans along the nation’s coasts to oil and gas exploration.
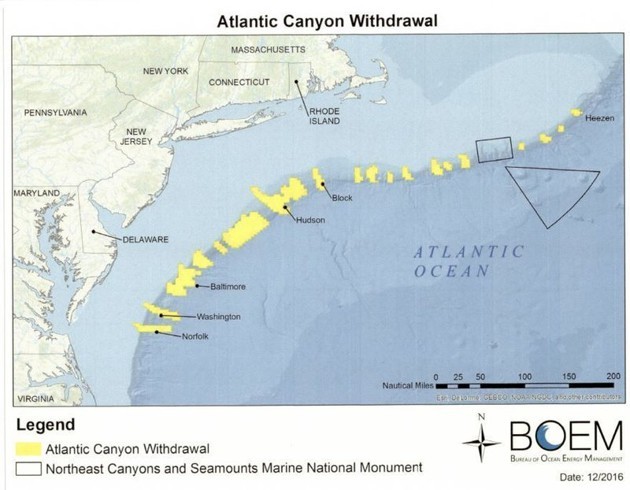
The White House announced that Obama invoked authority granted by the Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act to withdraw the Chukchi Sea Planning Area, most of the Beaufort Sea Planning Area, and 5,990 square miles of canyons in the Atlantic Ocean between New England and the Chesapeake Bay from fossil fuel activities.
Obama said in a statement that his decision was motivated by a desire to “protect a sensitive and unique ecosystem that is unlike any other region on earth.”
“They reflect the scientific assessment that, even with the high safety standards that both our countries have put in place, the risks of an oil spill in this region are significant and our ability to clean up from a spill in the region’s harsh conditions is limited,” Obama explained. “By contrast, it would take decades to fully develop the production infrastructure necessary for any large-scale oil and gas leasing production in the region – at a time when we need to continue to move decisively away from fossil fuels.”

-
Map courtesy U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management
The OCLA was enacted in 1953. Section 12(a) of OCLA, 43 U.S.C. § 1341(a), provides that “[t]he President of the United States may, from time to time, withdraw from disposition any of the unleased lands of the outer Continental Shelf.”
The statute imposes no constraints on the President’s authority to order such a withdrawal. In that way it is similar to the American Antiquities Act of 1906, which gives Presidents the power to declare national monuments.
In both cases, Congress delegated its power over federal property to the President, but the grant could well be interpreted by a federal court as a “one-way ratchet” that does not permit a later President to reverse a predecessor’s decision to withdraw OCSLA areas from energy exploration activities.
The reach of section 12(a) has not been tested in litigation.
John D. Leshy, a professor of law at Hastings College of the Law in San Francisco and a former solicitor of the Department of Interior, told Atlantic Monthly that he believes Obama’s decision should be upheld in federal court if it is challenged by fossil fuel advocates.
“I think it was quite a realistic thing that Obama did, and it should be upheld—but who knows,” he said.
Congress could, of course, pass a bill reversing Obama’s move, but that legislation would have to clear a likely filibuster by U.S. Senate Democrats on the way to Trump’s desk.
-
Map courtesy U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management
Presidents also have authority under OCLA to craft five-year exploration plans. Obama has used that tool, too, as a way of reducing the American fossil fuel footprint in sensitive marine areas.
On Nov. 18 the administration issued the final five-year OCLA lease program that covers the years 2017-2022. It proposes one sale in waters off Alaska, in Cook Inlet, and none in the Atlantic or Pacific Oceans. The 2017-2022 lease program anticipates 10 sales of exploration rights in the Gulf of Mexico.
Canada also undertook action to ban future fossil fuel exploration in the Arctic on Dec. 20. Prime Minister Justin Trudeau announced that his country would impose the prohibition for five years.
“Canada is designating all Arctic Canadian waters as indefinitely off limits to future offshore Arctic oil and gas licensing, to be reviewed every 5 years through a climate and marine science-based life-cycle assessment,” Trudeau said in a joint statement by Canada and the U.S.
No Canadian oil and gas activity in the Arctic has occurred since 2006.
Alaska and other states retain authority to authorize oil drilling in the first three miles of ocean beyond their shores as management of those areas of the continental shelf are entrusted to them and is not subject to federal control.